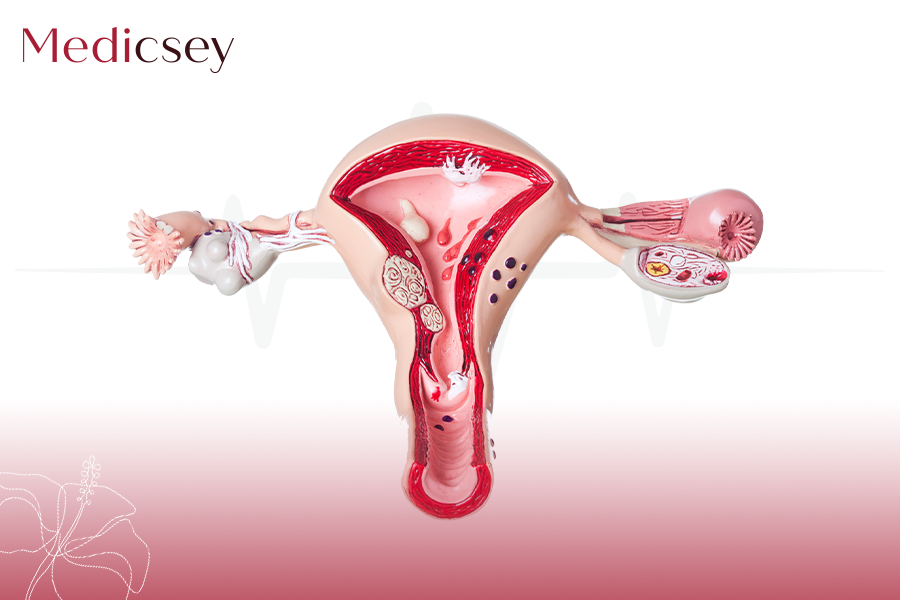
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a hormonal imbalance that usually begins at puberty. The condition interferes with normal reproduction. Symptoms include irregular periods, abnormal hair growth, and obesity.
What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a hormonal imbalance that interferes with normal reproductive processes. PCOS usually starts at puberty and is associated with irregular periods and other hormone-related symptoms.
The most concerning issues with PCOS are the increase of infertility, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, and the higher risk of developing endometrial (uterine) cancer at an early age.
What causes polycystic ovary syndrome?
Research is ongoing to uncover a cause for PCOS. There is evidence that shows a link between certain forms of PCOS and family history, suggesting a genetic basis for the condition.
What are the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome?
- Irregular menstrual periods, or no menstrual periods at all
- Decreased frequency or complete lack of ovulation, resulting in problems with infertility
- Obesity, often specifically characterized by weight gain in the upper body and abdomen
- Oily skin and hair and persistent acne into adulthood
- Abnormal hair growth, in a masculine distribution (facial hair, heavy hair growth on arms, chest, and abdomen)
- Tendency to develop type 2 diabetes








.png)
.webp)

.webp)

.webp)